Carotid artery disease may be asymptomatic (without symptoms) or symptomatic (with symptoms). Asymptomatic carotid disease is the presence of a significant amount of atherosclerotic build-up without obstructing enough blood flow to cause symptoms. However, a sufficiently tight stenosis will not always cause symptoms. Symptomatic carotid artery disease may result in either a transient ischemic attack (TIA) and/or a stroke (brain attack).
A transient ischemic attack (TIA) is a sudden or a temporary loss of blood flow to an area of the brain, usually lasting a few minutes to one hour. Symptoms usually go away entirely within 24 hours, with complete recovery. Symptoms of a TIA may include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Sudden weakness or clumsiness of an arm and/or leg on one side of the body
- Sudden paralysis (inability to move) of an arm and/or leg on one side of the body
- Loss of coordination or movement
- Confusion, dizziness, fainting, and/or headache
- Numbness or loss of sensation (feeling) in the face
- Numbness or loss of sensation in an arm and/or leg
- Temporary loss of vision or blurred vision
- Inability to speak clearly or slurred speech
TIA may be related to severe narrowing or blockage or from small pieces of an atherosclerotic plaque breaking off, traveling through the bloodstream, and lodging in small blood vessels in the brain. With TIA, there is rarely permanent brain damage.
Call for medical help immediately if you suspect a person is having a TIA, as it may be a warning sign that a stroke is about to occur. Not all strokes, however, are preceded by TIAs.
Stroke is another indicator of carotid artery disease. The symptoms of a stroke are the same as for a TIA. A stroke is loss of blood flow (ischemia) to the brain that continues long enough to cause permanent brain damage. Brain cells begin to die after just a few minutes without oxygen. The area of dead cells in tissues is called an infarct.
The area of the brain that suffered the loss of blood flow will determine what the physical or mental disability may be. This may include impaired ability with movement, speech, thinking and memory, bowel and bladder function, eating, emotional control, and other vital body functions. Recovery from the specific ability affected depends on the size and location of the stroke. A stroke may result in problems such as weakness in an arm or leg or may cause paralysis, loss of speech, or even death.
The symptoms of carotid artery disease may resemble other medical conditions or problems. Always consult your physician for a diagnosis.
FAQ
How does the carotid artery become blocked?
The carotid artery is responsible for supplying blood to the brain. Blockages in the carotid artery are the result of fatty deposits called plaque within the artery. While most of these plaques remain asymptomatic, some may break, causing a small particle to dislodge, travel up an individual’s bloodstream and into his or her brain. This can block off a small branch within the brain and eventually result in a stroke.
What are the risk factors associated with the build up of plaque in the carotid arteries?
Several risk factors associated with the build up of plaque in the carotid arteries include:
- Age (if an individual is over 50 years old)
- High cholesterol
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Gender (if an individual happens to be a male)
This does not mean that individuals outside of these categories are not at risk, but the group that meets these criteria is at a much higher risk of developing blockages in the artery than the average person.
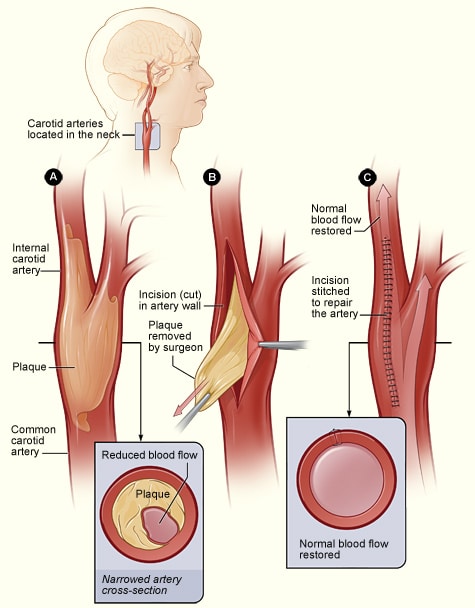
What is a carotid endarterectomy?
A carotid endarterectomy is one method of preventing a stroke in individuals who happen to have a carotid plaque. It is a relatively straightforward procedure that was first performed in 1953 and has since been perfected through multiple improvements in surgical technique and technology and other improvements in anesthetic care.
Are there any risks associated with this procedure?
There is a very small risk, usually to the amount of three or four percent, of developing a stroke because a little piece of the plaque may dislodge while the procedure is being performed. However, most of these strokes are small and do not last very long.
What can patients expect during the recovery process?
Most patients stay in the hospital overnight and are discharged the next morning. Patients can anticipate returning to work and other normal activities within 2-3 weeks after the procedure. Because the incision is small, it heals very well and leaves only a very small scar that is usually imperceptible to others.
How is this procedure performed?
Most of these procedures are performed under general anesthesia; however, they can be performed under local anesthesia, too. The procedure involves having a vascular surgeon make a very small incision, anywhere from 2-3 inches long, on the front and side of your neck to expose the artery. Once the artery has been exposed, the surgeon will place a little shunt that will continue to provide blood flow to the brain while he or she opens up the artery and removes the plaque. Once the plaque has been removed, the surgeon places small patch before closing the artery to widen the artery and re-established blood flow to the brain.
What should individuals with these risk factors do?
Individuals who are concerned that they may be at risk for developing blockages in their carotid artery should discuss with their physician the possibility of being screened to look for blockages in their carotid artery.
Schedule a Carotid Artery Consultation
If you believe you are exhibiting the symptoms of carotid artery disease, contact our office in the Glendale, Scottsdale, or Phoenix, AZ areas to schedule a consultation with a specialist. You can call our office at (623) 258-3255 or complete an online contact form and an associate will be in touch with you.